The Castle Rock levee system - geotechnical aspects
The Castle Rock levee system is described in detail in a report by the US Army Corps of Engineers Cowlitz River Levee Systems 2009 Level of Flood Protection Update Summary available at
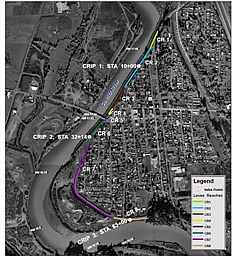
Index map of segments studied
[click for full-sized version]
The levee system includes segments at Castle Rock, Lexington (which experienced sand boils in the 1997 flood), at Kelso, along the Coweeman River, and at Longview. For the Castle Rock segment, soil parameters were as follows:
Slope stability and seepage parameters for Castle Rock Levee |
||||
Embankment fill |
||||
drained friction angle |
37 |
45 |
degrees |
|
moisture |
7 |
14 |
% |
|
moist unit weight |
137 |
150 |
pcf |
|
permeability, sand and gravel |
1.02E-03 |
cm/s |
||
permeability, quarry waste |
5.08E-02 |
cm/s |
||
Foundation soils |
||||
drained friction angle, poorly grades sand and silty sand |
34 |
37 |
degrees |
|
drained friction angle, gravels and sand with gravel |
41 |
45 |
degrees |
|
moisture |
15 |
30 |
% |
|
moist unit weight |
118 |
136 |
pcf |
|
permeability |
2.00E-04 |
3.00E-04 |
cm/s |
|
horiz k/vert k |
4 |
|||
Factor of safety for levee failure:
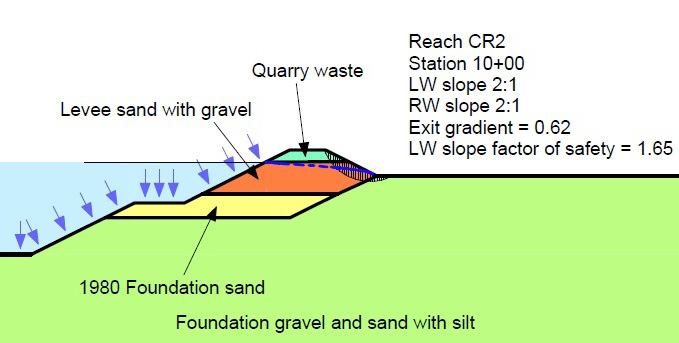
Seepage and slope stability calculations for levee reach CR2 give a 1.65 factor of safety with water elevation at 57.4 feet.
Other data sources
http://www.nwp.usace.army.mil/docs/d_msh/Final_Cowlitz_LOP_02-04-10.pdf
http://www.nwp.usace.army.mil/docs/d_msh/Cowlitz_levees_safe_water_level2010.pdf
http://www.nwp.usace.army.mil/docs/d_msh/Toutle-Cowlitz_sediment_budget.pdf